Everything You Need to Know About Hybrid Batteries, Part 1
 Hybrid cars are amazing. Whether it’s a standard hybrid (HEV), also referred to as a full- or self-charging hybrid, or a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), their growing popularity means more people are owning hybrid cars than ever before.
Hybrid cars are amazing. Whether it’s a standard hybrid (HEV), also referred to as a full- or self-charging hybrid, or a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), their growing popularity means more people are owning hybrid cars than ever before.
That said, in the shop we often receive questions about the batteries in these vehicles, so we’re diving in here in this two part series to give you more info on hybrid batteries.
In Part 1, our focus is on reviewing the two different types of hybrid vehicles, as well as the different types of batteries hybrids use.
Let’s jump in!
 How Many Types of Hybrid Vehicles are There?
How Many Types of Hybrid Vehicles are There?
So, it’s common knowledge that a hybrid vehicle utilizes both gas and electricity to run. But did you know there are two different types of hybrid vehicles?
STANDARD HYBRIDS (HEVs)
This type of hybrid features self-charging batteries. This works through what’s called “regenerative braking,” as well as getting recharged by the gasoline engine.
And if you’re wondering, HEVs never have to be plugged in.
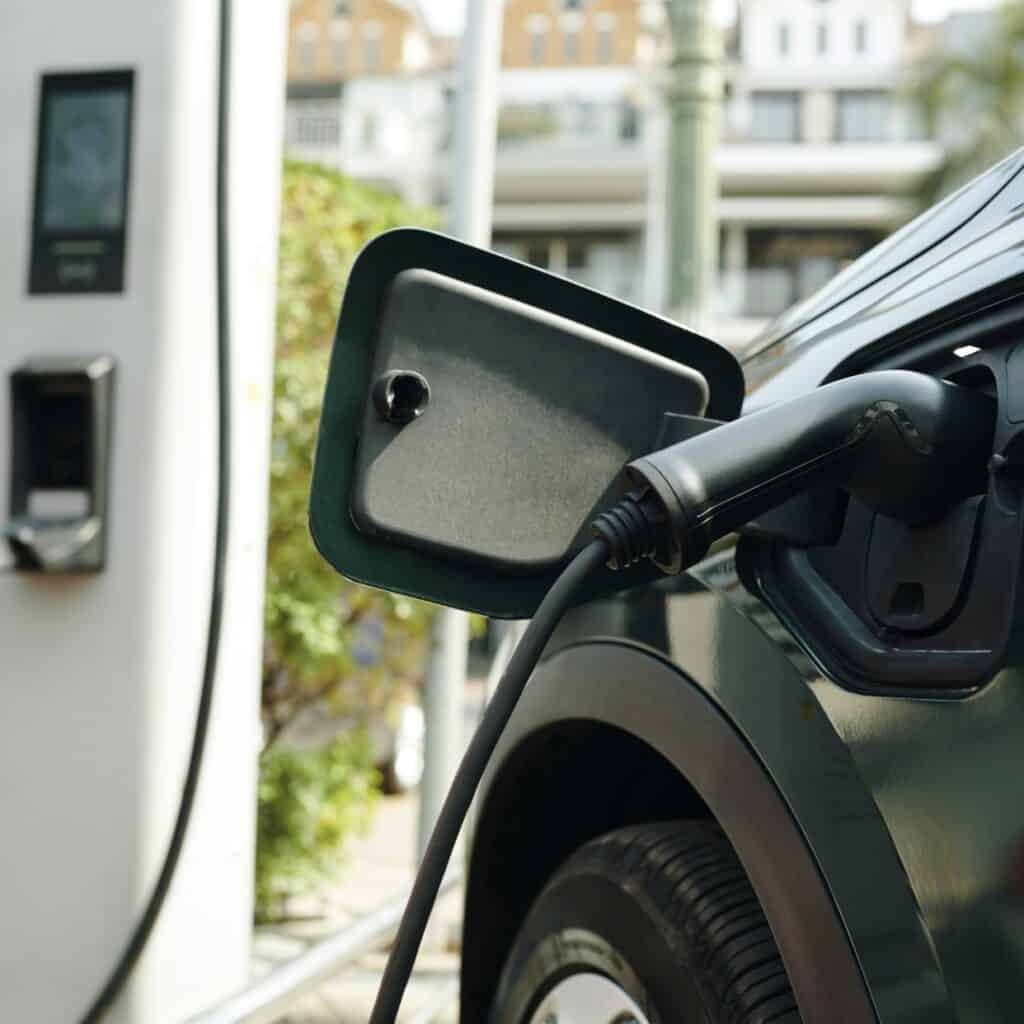 PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES (PHEVs)
PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES (PHEVs)
PHEVs are made with bigger batteries, and have a more substantial “electric-only range.” In contrast to HEVs, PHECs do need to be plugged into an external charging apparatus (IE: a public charging station, wall outlet, or home station.
With home charging, you can simply utilize a standard home outlet (120-volt). You can also make use of a faster home charging station (240-volt).
Battery Types
Although there are a handful of different hybrid battery types, there are two kinds that are widely used, and we’ll stick to these in today’s article.
 NICKEL-METAL-HYDRIDE (NiMH) BATTERIES
NICKEL-METAL-HYDRIDE (NiMH) BATTERIES
NiMH batteries are non-flammable, can withstand a wider range of operating temperatures, and are less expensive to produce and recycle. That said, they are a heavier weight, less powerful — plus they generate significant heat at high temperatures.
LITHIUM-ION (Li-ion) BATTERIES
Li-ion batteries provide a higher energy density, and this provides a hybrid vehicle with improved better acceleration — plus better energy storage. This all adds up to improved fuel efficiency. Li-ion batteries are also more compact and less heavy in comparison to NiMH batteries. As you might imagine, with these benefits comes a higher cost. Li-ion batteries also have a shorter lifespan than NiMH batteries.
This brings us to the end of Part 1 of our series. In Part 2, we’ll continue our discussion on everything you need to know about hybrid batteries, turning our attention to maintenance, expected service & how often a hybrid battery needs replacement.
Get in Touch
If you have any questions about hybrid cars, or anything auto related, feel free to contact us anytime! In addition, you can schedule a service online by clicking on the “Request Appointment” button in the navigation above. See you on the road!
 How Many Types of Hybrid Vehicles are There?
How Many Types of Hybrid Vehicles are There?